Search engine optimisation is the process of optimising your site for search engines so that it receives more traffic, ranking, and potential sales. It makes your website easier to find against relevant keywords on search engines like Bing, Ask, AOL, and Google, and provides a better overall user experience.
An SEO strategy is commonly associated with creating high-quality content written around specific keywords, optimising it for search engines and end-users, and building website authority by optimising social media platforms and backlinking.
A Brief History of SEO
The concept of SEO emerged coinciding with the launch of the first search engines, though SEO as we know it today was non-existent.
1991 till 1997:
The first website was launched in 1991, and from 1994 to 1997, many search engines like Yahoo, AltaVista and Lycos were launched. They followed SEO on a very basic level, such as using keywords in tags and content.
SEO was first coined in the marketing material of Multimedia Marketing Group in 1997, but search engines still depended on directories.
1998:
The juggernaut that later came to be known as the Google search engine was launched in 1998, and its algorithm, PageRank, changed the game. It considered external links a ranking factor and website importance.
2001 till 2003:
From 2001 to 2003, various SEO terms were coined, such as search engine placement, website promotion, and search engine strategies, hinting at formally establishing the industry.
Besides this, launching tools like Google Toolbar and AdSense fueled the rise of monetised SEO-based content. The Google algorithm, Florida, was launched and designed to hit all sites with poor backlinks. This launch also shaped the trajectory of SEO, providing guidelines for link analysis.
2004 till 2007:
In 2004, Google started personalising results, which served as the foundation for local SEO. Until now, SEO was based on practices like keyword stuffing and optimising meta tags, which gave birth to low-quality spammy content.
But the TrustRank algorithm went a step ahead of Florida and filtered out all the spam and black hat SEO techniques. This gave website owners a set of instructions regarding good practices.
From 2004 to 2007, Google focused on launching new tools like Google Analytics and Google Webmaster and algorithms like Big Daddy, which enhanced the scope of high-quality content and link-building strategies.
2010:
This year, Google introduced Caffeine, which enhanced the capacity for article indexation. Because of this, search results were capable of prioritising fresh content.
2011:
2011 proved havoc for many websites as Panda algorithms hit the market and brought an unusual upheaval. This allowed search engines to filter out low-quality content.
When Google Freshness was launched, Caffeine improved. This helped websites and content like good timeless recipes stay updated, prioritising fresh and relevant content. This was a time when website owners learned they needed to update their content regularly, which is an essential SEO practice today.
2012:
Google Penguin weeded out web spam content in 2012. You need to align your web with Google’s Webmaster Guidelines or Search Essentials. Penguin scans for potential violations like link schemes and keyword stuffing, which were widely used to gain quick ranking.
The difference between Penguin and Panda was that the former analysed the quality of links while the latter focused on the quality of content.
2013:
With the dusk of 2013, Google Hummingbird hit the search engines playground and introduced NLP in web content and search queries. This was again a hit on keyword stuffing and prioritised natural language content.
This laid the groundwork for future AI- and NLP-based searches.
2015:
This year was a breeze for mobile-based searches with Google Mobilegeddon. Websites optimised for mobiles received a huge boost and became a never-ending necessity.
As already mentioned, Google was becoming the big giant in the search engine field, so all the major updates were centred around it.
2015 saw two updates, the second of which was Google RankBrain. This allowed Google to make intelligent searches based on the search query provided to them. It analyses how users interact with a search query and learns to improve in the future.
2016:
Google came up this year with a moment of happiness by launching Google Possum. This improved the search queries based on the local from where they are being made. Local businesses were connected to the local audience.
This gave rise to a new category in SEO, i.e. local SEO.
2017:
Websites relying on black hat SEO techniques saw a huge dip after 2017, when Google Fred was implemented. Google was becoming harsher on poor websites every day, penalising sites with an overabundance of ads and thin content.
Semantic search was prioritised to improve user experience, and by the 2020s, AI, machine learning, and voice search were becoming everyday searches used by end users. Schema markups and rich snippets were increasingly the centre of attention of SEO.
2019 – 2021:
SEO professionals’ attention shifted toward Mobile-first indexing and page speed, which highlighted the importance of mobile responsiveness and fast-loading websites.
Google BERT was built upon the Hummingbird algorithm, which prioritised long-form keyword research and user search intent. It improved search quality and prioritised relevance.
2023:
Google Gemini came to the surface and worked alongside BERT to utilise its power of generative tasks and artificial intelligence. Understanding the intent helps answer complex search queries and can conduct sophisticated conversations.
How the History of SEO is Affecting the Future?
SEO has inculcated technologies like artificial intelligence, voice search, and augmented reality, and it will keep adapting to the latest technology. The future of SEO could be something like this:
- More focus on improving the user experience.
- Quality would stay the focus.
- Machine learning and AI would increasingly be sophisticated, providing a more relevant and seamless experience.
How SEO Differs from SEM and PPC?
Let’s start by defining the terms. SEO has already been determined so that I will skip that.
What is SEM?
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is a strategy for increasing your website’s visibility on search engines. It might use SEO or PPC. It offers the following advantages:
- Improve the ranking of your website in search engine result pages.
- Enhance your visibility, attract the right customers and boost your sales.
- Build brand awareness and credibility.
What is PPC?
Pay-per-click is a strategy where you must pay for every click on your ad. These ads appear on top and bottom of a SERP. Its benefits include:
- Different campaigns are available based on your business and interest.
- Measurable and quick results.
- Controllable and testable campaigns.
- Algorithmic changes don’t affect campaigns.
Difference Between SEO, SEM, and PPC
The difference between all these three terms is quite evident.
SEM includes all the results shown on SERPs, regardless of whether they are paid or unpaid. So, the focus is on combining SEO and paid advertising, while it can be paid or unpaid (as SEO and PPC are both included in it).
It offers long—and short-term ranking strategies, and the goal is to increase a site’s visibility. So it can be confidently said that,
SEO + PPC = SEM
The real difference lies between SEO and PPC. SEO focuses on ranking the website organically based on keywords using techniques like high-quality, optimised content, core web vitals, mobile friendliness, and so on.
Contrary to this, the focus of PPC is to gain a temporary paid ranking on certain keywords, where advertisers pay every time a customer clicks on their ad, whether the customer converts or not.
If we talk about results, we have to have some patience to bear the fruits of SEO, whereas PPC lets you enjoy results immediately. These immediate results are a little costly, but you only have to pay for the premium tools if you do SEO yourself. So, the strategy in SEO is long-term content-focused, while in PPC, it is immediate and budget-driven.
Why SEO is Important?

To connect efficiently and cost-effectively with its audience, the website must rank higher and enhance its brand awareness. SEO is one of the few models that can achieve this aim, so the need for quality work keeps increasing.
A few other reasons why SEO is important are as follows:
A Lot of Traffic
Billions of search queries are being made every day, and if your website ranks on keywords, it will enjoy a lot of traffic.
Around 50% of visitors skip the PPC ads and jump directly on organic results. So you must gather the clicks on your website; otherwise, your competitors definitely will. SEO roots back from the 1990s and is a tested way to collect clicks.
Trust and Credibility
Building trust and credibility online and offline takes time and effort. It is earned and built over time. AI has made it even harder, as processes are quite easy to follow.
Such credibility cannot be owned with strategies like PPC. Though they promise immediate results, you will lose all the ranking once you stop paying for these campaigns. Besides this, people don’t consider ads trustworthy.
Contrary to this, as SEO is advancing, Google has introduced the E-E-A-T principle, which simply means that websites showing Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness are going to be ranked.
You could only show these characteristics if you are someone really into business. Spammy content and quick ranking schemes need to fulfil Google’s EEAT principle.
Let me rephrase it another way; There are 10 ways to develop trust:
- Value long-term relationship
- Be honest
- Honour your commitments
- Admit when you are wrong
- Communicate effectively
- Be vulnerable
- Be helpful
- Show people that you care
- Stand up for what’s wrong
- Be transparent
If you go through the history section again and understand the EEATs principles, you will notice that, over time, SEO catered to all of these in one way or another.
On top of that, SEO is a slow game that requires you to show up consistently, take care of your site and Google Algorithms, and, most importantly, serve the users right.
Thus, websites that rank 100% of the time already have trust and credibility factors under their belts. If a bad website ranks, Google will sooner or later realise and de-rank it.
Better User Experience
In the realm of web search, everybody dreams of getting the top spot and staying there, but only some understand that out of many factors, one of the major is user experience.
Search engines are now smart enough to measure user experience in real-time. Every marketer needs to adhere to updates like Google Page Experience.
When it comes to marketing, two major ways to rank a website are PPC and SEO. The ranking gained from PPC is budget-based. The more budget you are willing to burn, the longer your website will rank.
But the moment you stop paying proves to be where you will lose your ranking.
Contrary to this, SEO works on different principles. Although there are many factors to take care of patiently, if you follow the right SEO practices and keep your website optimised, you will gain a permanent ranking.
Another major difference between these two marketing strategies is their focus on user experience. PPC focuses on getting the user to click on your site and generate sales, but in SEO, you have to prove to search engines and end users that you are trustworthy and can add value to their lives.
SEO professionals intend to quickly and efficiently provide high-value-driven content their audience seeks.
Increased Engagement and Conversion
There are various types of engagement and multiple metrics to track them. Whether it is pageviews, top content, new vs returning visitors, bounce rate or time on site, SEO easily caters to all of them.
- SEO focuses on metrics that speed up your site and make it more responsive. It eradicates all the factors that make your landing page slow and non-responsive, thus directly affecting your conversion.
- SEO also take care of technical errors like 404 or 301 redirects. This doesn’t hurt the user experience and redirects potential customers to the right place.
- It also focuses on producing real-time quality content that serves the user. Over the period, if you maintain such consistency, you would stick to the users’ minds as trustworthy and authoritative.
There are many other reasons why SEO enhances engagement and conversion, like clean navigation and site design, improved internal linking and social media presence, seeding out clear CTAs in an organic manner and helping collect email addresses, which could lead to another way of generating money, i.e., email marketing.
Impact on the Buying Cycle
If you follow best SEO practices, you have already maintained yourself as an authority. At this point in your journey, you can reap the fruits of your authority and trust.
You can negotiate good deals and offer better quality products and services, and the customer will be more than happy to buy from you.
Constantly Changing and Evolving
Constant change is the new permanent, and with Google periodically releasing updates, SEO professionals cannot sleep on websites.
They must constantly update their content and look for possible burnout, just like a mother saves her kid from potential harm. Obviously, I am talking about a good SEO expert who really cares about his website.
Another proven fact in SEO is that users want updated content, and we know that users are the ultimate kings in the online realm. So, SEO is important as it promises continuous updates and changes.
Cheap and Cost-efficient
Compared with PPC, SEO is cheap and cost-efficient in the grand scheme of things.
For every click in PPC, you burn money, but in SEO, if you do it yourself, you will only pay for the premium tool you need. Even if you hire an expert like Brandix Soft, the packages are highly economical and have top-notch services. They would have access to advanced tools and a team of experts who would care for everything.
Long Term Strategy
One of SEO’s beauties is that it is a long-term game. Many of you consider that an utterly negative thing, as you would have to wait to bear the fruits.
In fact, SEO is all about building a brand and a business that can bear fruit in the long run. It elevates your status to a spot where people trust you and consider you credible and trustworthy. They would be more willing to buy from someone who gives them genuine information consistently and doesn’t bluff.
Measurable Results
Although SEO provides a different, yet readily quantifiable, ROI than paid search, it can be assessed with the right tracking and analytics. The primary challenge with SEO is that no clear method correlates actions and their results.
Nonetheless, tracking and technological advancements will support SEO specialists in their endeavours. Good SEO professionals concentrate on improving performance by understanding how particular actions should impact it. Thus, brands must also grasp digital performance to prove their success, particularly concerning SEO.
What are the Types of SEO?
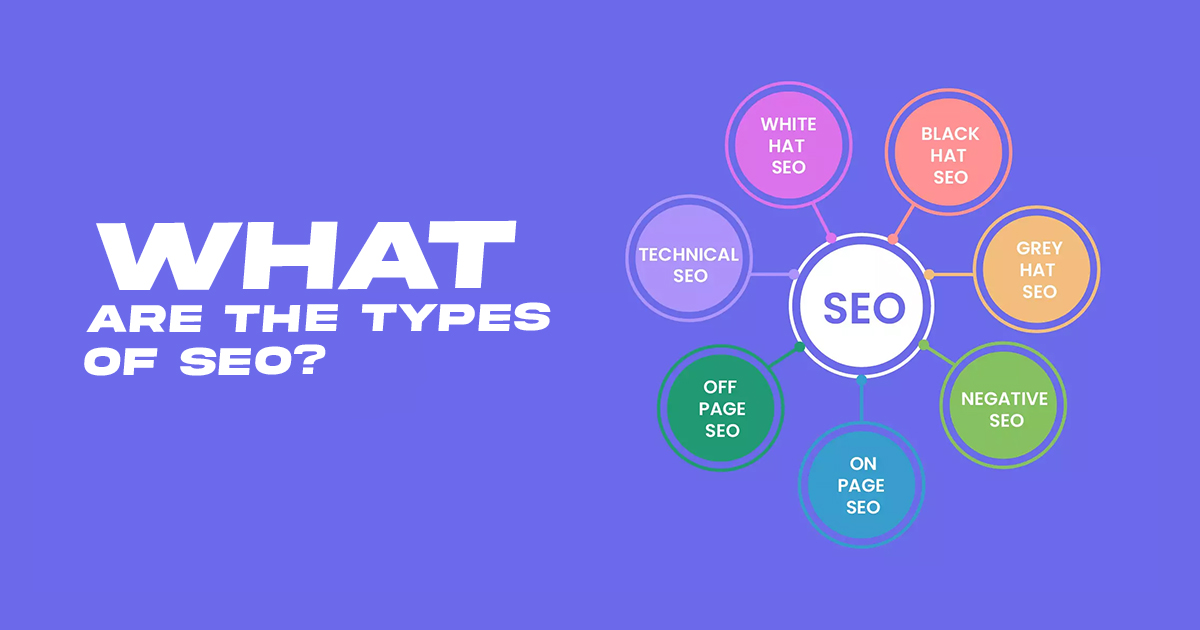
SEO can be divided into many categories, based on the areas it covers, its scope, or the practices it follows. Let’s explore each one a bit to understand the difference.
SEO based on Search Engine Areas it Deals with
Many areas of SEO are related to the search engine. These include:
On-page SEO
This includes the process of optimising webpages for search engines and the end users. The practices followed in this type of SEO are:
- Site content
- Keyword research
- Tags optimisation
- Meta description
- URL optimisation
- Featured snippets
- Site architecture
- Media files, including videos, images and audio optimisation
Off-page SEO
This includes all the activities done outside of the website to create its authority and impact the ranking on SERP. These activities include but are not limited to:
- Backlinking
- Content marketing
- Local SEO
- Social media profile activity
- Guest posting
- Brand mentions
- Influencer marketing
Technical SEO
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimising your site according to Google’s guidelines and the needs of end users. The aspects include:
- Fixing broken links
- Using an SSL certificate to secure your site
- Optimise site structure and sitemap
- Write and submit the robots.txt file
- Fix crawling issues
- Ensuring the site is mobile-friendly

SEO Based on Scope
Based on scope, SEO can be divided into the following types:
Local SEO
This type of SEO follows a set of techniques that help local businesses gain more visibility in Google searches, including local intent and map sections.
Beside many of the commonalities, local SEO differ from other type of SEO by their focus on:
- Optimising map section
- Getting more reviews
- Get your site listed on directories and maintain NAP consistency
International SEO
International SEO refers to optimising your site for different languages and countries. Compared to local SEO, the horizon of international SEO is huge.
As this SEO type goes beyond the border, a few of the practices that make it different from other types include:
- Targeting multiple languages and multiple countries
- Using country-specific domains and subdomains
- More complex site structure supporting different regions and languages
- Complying with international laws
- Using one language per page
- Implementing hreflang properly
E-commerce SEO
E-commerce SEO refers to optimising an e-commerce-based website to gain traffic at a much lower cost. Your website must appear in search results to reach potential customers; without visibility, you can lose them.
SEO Based on Practices Followed in the Market
Based on practice, SEO can be divided into three types:
White Hat SEO
White-hat SEO refers to complying with the guidelines established by search engines like Google. It all comes down to boosting your ranks while adhering to search engine criteria and maintaining your integrity. Long-term success for your website is guaranteed when you use white-hat SEO. Here are some crucial processes:
- Make use of appropriate keywords in descriptive meta tags.
- Provide your audience with top-notch services and content.
- Make your website straightforward and user-friendly.
Black Hat SEO
Black-hat SEO uses strategies to alter Google’s algorithm to get fast results. This includes tactics like cloaking, keyword stuffing, and sponsored links. These strategies may produce quick results, but when Google notices, they might hurt your website. Black-hat SEO should always be avoided to avoid any charges.
Gray Hat SEO
Gray-hat SEO lies between white-hat and black-hat SEO. It is riskier than white-hat techniques because the regulations governing it are not clear.
Although using grey hat techniques will not block your website, it’s still unsafe. Understanding these techniques enables you to avoid possible dangers and concentrate on moral tactics to preserve your website’s traffic and reputation.
How SEO Works?

SEO involves enhancing a website’s content, employing relevant keywords, and obtaining high-quality backlinks to grow its rating and exposure on search engines. Results may begin to show up once a page is crawled and indexed by search engines, but it frequently takes months for the entire impact to manifest.
Rankings
Rankings decide where a webpage shows up on search results. They start at position zero and go down the list. A page can hold only one position at a time. Rankings can change due to competition, the page’s age, or updates in search engine algorithms.
Visibility
Visibility shows how often your website appears for relevant searches. If your site has low visibility, it doesn’t appear for many searches. Higher visibility means more exposure and chances of getting clicks.
Both rankings and visibility help achieve SEO’s main goals: driving relevant traffic and building your website’s authority.
Key Elements of SEO

SEO is a long-term game; you must build a strong foundation to see results and thrive. Although there are more than 200 unsaid factors to take care of (they are unsaid as no search engine has announced them, but according to professionals, these factors do matter). A few essentials are as follows:
Crawlability and Indexability:
You can understand crawlability and indexability as a road map or guideline for searching, going through, and placing a box according to its topic and genre. If search engines find it hard or cannot find your content, they won’t be able to show it to them. Fix this issue by:
- Upload a sitemap and robots.txt and set up a Google Search Console account to help Google find your site and content.
- Connect your pages internally so search engines can flow between pages and find new ones easily.
High-quality Content
Upload high-quality content as it builds trust, credibility and authority among your followers. Focus on providing:
- Accurate and factful helping information.
- Avoid spammy or plagiarised content
- Write naturally, and don’t stuff keywords
Keyword Usage
Based on the keyword used inside your content, it ranks against certain queries on search engines. Use keywords naturally in your:
- Titles and meta tags/descriptions
- Headings.
Search Intent
You need to understand the psychology behind why a user is searching for something and what he possibly would be looking for. Examples could include:
- Informational keyword that answers a specific query.
- Navigational keywords that help users find specific pages.
- Transactional keywords that are used by users with the intent of buying something.
EEAT
EEAT stands for Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trustworthiness. Search engines like Google highly emphasise websites with these four characteristics. These are specifically crucial for health, finance or life decision-based websites.
Backlinking
You would need to build backlinks from reputable websites in your niche. This is another crucial element of successful SEO. You can earn backlinks by:
Creating high-value content that others can relate to and rely on.
Writing guest posts on relevant sites and gaining backlinks.
Social Signals
Social signals alongside backlinking are crucial off-page factors that help build credibility in the eyes of search engines and users. You can gain social signals via:
- Staying active on your social media handles.
- Post quality content and engage with your users.
- Adding social buttons to your website.
- Build a following that can suggest you online somewhere to someone.
How Long Does SEO Take to Show Results?
SEO takes at least 3 to 6 months to show results. But if you are working on international SEO, where competition is cutthroat, it can take 1 to 2 years to rank on the first page and among the top spots.
Having said that, I am again emphasising that SEO is a long-term strategy. You constantly need to keep your content and website optimised and updated. Creating such new high-quality content and maintaining older ones optimised is an ongoing process that demands time and patience.